User Concept and Multitenancy
User Concept
Central ServerŪ supports two user types: System Users and standard users. System Users are special users as they may perform all available operations, regardless of required privileges, whereas standard users are not allowed to perform operations without owning the required privileges. Therefore, privileges allow standard users to perform particular operations. Users and privileges are subject of the User Management web application.
Multitenancy
All Central Server web applications support multitenancy with respect to Customers. Each standard user is assigned to one
Customer - i.e. a tenant. Thus users are able to view and manage data of their own Customers only and are never able to
view or manage resources of different Customers. Users may view their Customers ( ) in the upper right user menu next to their login name (
) in the upper right user menu next to their login name ( ).
).

Logged in System Users may operate on behalf of only one Customer at a time. Therefore, System Users must switch
the Customer to view resources of a different Customer. For a Customer Switch System Users need to select a
Customer within the upper right user menu. Left-clicking the small arrow next to the current Customer ( ) left to the System User's login name opens a drop-down box
allowing the selection of another arbitrary Customer.
) left to the System User's login name opens a drop-down box
allowing the selection of another arbitrary Customer.
The Customer Switch drop-down box contains the special menu item [System], which is visible to System Users only. The [System] context enables System Users to execute web applications in a System context for system administration purposes. Thus some entities do not exist within the System context and System Users will see a warning if they try to use such entities. Within the System context, System Users may see entities of different Customers in the same view. This is necessary to manage the respective web applications in the context of System administration.
After a Customer has been selected, the respective web application reloads its views and operates in the context of the selected Customer.
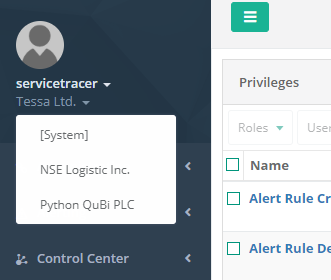
To stress the distinction of standard users and System Users with respect to multitenancy: standard users may only view the Customer they are assigned to and are not able to switch to different Customers; whereas System Users only view the currently active Customer, but are able to switch to other Customers. This distinction is reflected in the upper right user menu: differing from the standard user menu, the System User menu displays a small arrow next to the Customer name. Clicking the arrow opens the drop-down box Customer Switch
| System User: | 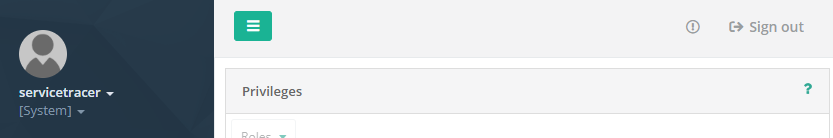 |
| Standard user: |  |
Some web applications are categorized as System web applications and thus are accessible for System Users only. System web applications do not display a Customer switch arrow in the upper right user menu.
Operational context
Each web application operates in one of two contexts: Customer context or System context. The two different operational contexts are explained below.
Customer Context
This is the default operational context
of a web application. A standard user operates in Customer context only, whereas a System User may operate in both Customer
and System context. System Users may switch between Customer and System context by means of Customer Switch. If
the Customer Switch specifies [System], logged in System Users operate in the System context. Otherwise,
logged in System Users operate in the context of the Customer specified.
System Context
This is a special operational context for
System Users only. If the Customer Switch specifies [System], logged in System Users operate in the system
context. Otherwise, logged in System Users operate in the context of the Customer specified.
